JAKARTA, cssmayo.com – Ever wonder why some folks, maybe like your parents (or let’s be real—us at times), wait until the last possible second to embrace new Techno gadgets? Laggards: The Last Adopters in the Technology Diffusion Cycle, that’s what they’re called. And honestly, I’ve definitely been there—clutching my old phone like it’s an ancient relic, even when all my friends are flexing the latest stuff.
In the realm of technology adoption, laggards are often seen as the last group to embrace new innovations. Typically characterized by skepticism and resistance to change, laggards can provide valuable insights into the adoption process and the challenges that come with it. In this article, I’ll explore the characteristics of laggards, share lessons learned from my experiences with late adoption, and discuss the implications for both individuals and organizations.
Understanding Laggards in the Technology Diffusion Cycle
Who Are Laggards?
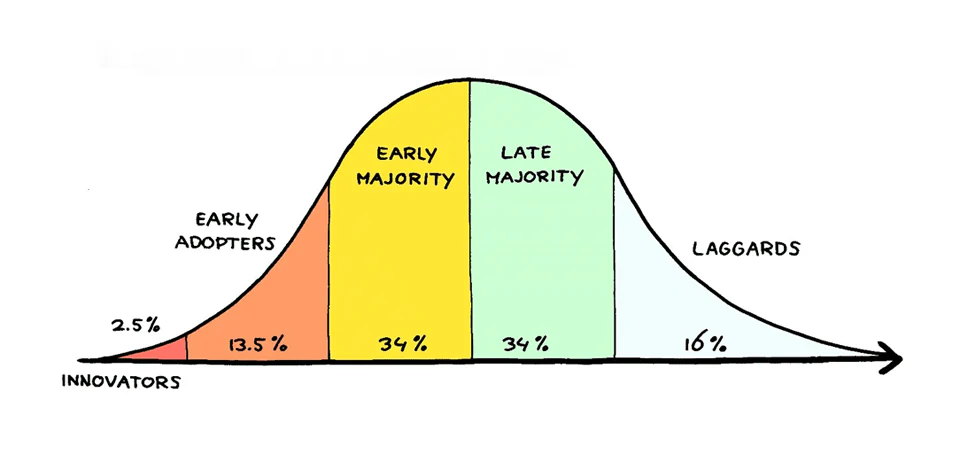
Laggards are the final segment in the technology adoption lifecycle, which includes innovators, early adopters, early majority, and late majority. This group is usually defined by:
- Skepticism Towards New Technology: Laggards tend to be cautious and often prefer established technologies that they are familiar with.
- Limited Resources: They may lack the financial means or technical knowledge to adopt new technologies quickly.
- Preference for Tradition: Laggards often value tradition and may resist change due to comfort with existing practices.
The Technology Adoption Lifecycle
The technology adoption lifecycle is a model that illustrates how different groups adopt new technologies over time. It typically follows this pattern:
- Innovators: The first to adopt new technology, often risk-takers.
- Early Adopters: More socially connected and influential, they help drive awareness.
- Early Majority: Pragmatic users who adopt once they see proven benefits.
- Late Majority: Skeptical individuals who adopt after the majority has done so.
- Laggards: Last to adopt, often only when necessary or when the technology becomes unavoidable.
Lessons Learned from Being a Laggard
1. The Cost of Waiting
One of the most significant lessons I learned as a laggard is that delaying adoption can lead to missed opportunities.
- Example: When smartphones first emerged, I hesitated to switch from my basic mobile phone. By the time I finally made the change, I realized I had missed out on numerous conveniences, such as mobile banking, navigation apps, and instant communication. This experience taught me that waiting too long can limit my access to beneficial tools.
2. The Importance of Research
As a laggard, I often found myself overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information available about new technologies.
- Lesson: Conducting thorough research before adopting a new technology is crucial. I learned to seek out reliable sources, read reviews, and consult with early adopters to understand the pros and cons. This approach helped me make more informed decisions when I finally decided to adopt new technologies.
3. Understanding the Risks of Obsolescence
Staying with outdated technology can lead to obsolescence, making it harder to compete or function effectively.
- Example: In my workplace, I was hesitant to switch to a new project management tool that many colleagues had already adopted. Eventually, I found myself struggling to collaborate effectively, as most of my team was using features that I didn’t have access to. This experience emphasized the need to stay current to remain competitive and efficient.
4. The Value of Incremental Change
Adopting technology doesn’t have to be an all-or-nothing approach; incremental change can ease the transition.
- Lesson: I found that gradually integrating new technologies into my routine helped reduce the anxiety associated with change. For instance, instead of switching entirely to a new software program, I started by using it alongside my existing tools until I felt comfortable making a full transition.
5. Learning from Early Adopters
Engaging with early adopters can provide valuable insights and support during the transition.
- Example: When I finally decided to upgrade my home office equipment, I reached out to colleagues who had already made the switch. Their tips and experiences helped me navigate the learning curve and avoid common pitfalls. This reinforced the idea that leveraging the knowledge of others can facilitate smoother transitions.
6. Recognizing the Need for Change
One of the most important lessons I learned is that recognizing the need for change is essential.
- Lesson: I often waited until a technology became unavoidable, such as when my old computer could no longer run essential software. This experience taught me to be proactive in assessing my technology needs and to be open to change before reaching a crisis point.
Conclusion
Laggards play a unique role in the technology diffusion cycle, often providing insights into the challenges and hesitations associated with adopting new technologies. My experiences as a laggard have taught me valuable lessons about the cost of waiting, the importance of research, the risks of obsolescence, the value of incremental change, learning from early adopters, and recognizing the need for change. Embracing these lessons has not only improved my personal technology adoption journey but also highlighted the importance of being open to innovation in an ever-evolving landscape. Whether you identify as a laggard or find yourself somewhere else in the adoption cycle, understanding these dynamics can empower you to make informed decisions and embrace the benefits of new technologies.
Elevate Your Competence: Uncover Our Insights on Techno
Read Our Most Recent Article About Standardization: Ensuring Compatibility and Efficiency in Technology Systems!