JAKARTA, cssmayo.com – Biometric Authentication: Enhancing Security Through Unique Biological Identifiers really feels like something out of a Techno thriller, doesn’t it? I remember the first time I used a fingerprint scanner to unlock my phone. Wild stuff! Back then, I still worried someone could easily bypass it, but now? Let me share what I’ve learned and why these unique biological identifiers are game-changers.
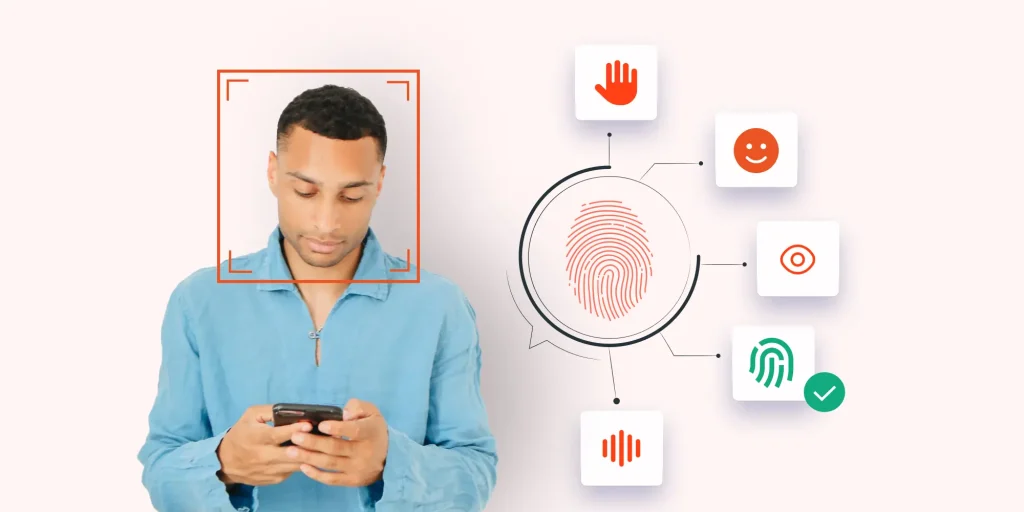
Biometric Authentication leverages physiological and behavioral traits—such as fingerprints, facial patterns, iris structures, and voice—to verify identity with a level of accuracy and convenience unmatched by passwords or tokens. From unlocking smartphones to securing border crossings, biometrics offer a frictionless yet robust layer of security for real, everyday safety.
How Biometric Authentication Changed My Life
When I first enabled fingerprint unlock on my phone, I never imagined how quickly I’d come to rely on biometrics:
- I no longer fumbled with PINs or forgot complex passwords.
- Mobile banking felt instantly more secure—my fingerprint became my strongest credential.
- At my office, door-access readers recognized me faster than any keycard, reducing queues and lost-badge incidents.
This seamless blend of convenience and security convinced me that biometric authentication is not just a futuristic novelty—it’s already integral to our daily routines.
Core Components & Technologies
- Enrollment & Template Creation
- Capture high-resolution scans of the user’s biometric trait.
- Generate a mathematical “template” (encrypted feature set) for storage.
- Sensors & Capture Devices
- Fingerprint scanners (optical, capacitive, ultrasonic)
- Facial cameras with infrared or 3D depth sensing
- Iris-recognition cameras using near-infrared illumination
- Microphones and motion sensors for voice and behavioral biometrics
- Matching Algorithms
- Feature Extraction: Identify minutiae points, ridge patterns, and key landmarks.
- Similarity Scoring: Compute a match score between live capture and stored template.
- Decision Thresholds: Determine acceptance or rejection based on false-acceptance (FAR) and false-rejection rates (FRR).
- Liveness & Anti-Spoofing Measures
- Detect fake fingerprints using pulse, temperature, or sweat pores.
- Use depth-map analysis and challenge-response prompts for face and iris scans.
Practical Applications
- Mobile Devices & Wearables
Unlock phones, authorize payments, and access health data with a glance or touch. - Financial Services
Secure ATM withdrawals, online banking, and contactless payments without cards. - Physical Access Control
Grant entry to offices, data centers, and high-security facilities with iris or fingerprint readers. - Border Security & Travel
Automated e-Gates speed up immigration by verifying passports and faces in seconds. - Workforce & Time-Tracking
Biometric clock-in/out systems eliminate buddy-punching and streamline payroll.
Best Practices for High-Trust Implementations
- Privacy by Design: Encrypt templates, store data locally or in secure enclaves, and comply with regulations (GDPR, CCPA).
- Multimodal Fusion: Combine two or more biometric factors (e.g., face + voice) to reduce spoofing risks and increase accuracy.
- Adaptive Thresholds: Dynamically adjust match thresholds based on risk level, device type, or user behavior.
- Regular Template Updates: Re-enroll periodically to account for aging, injuries, or device changes.
- User Education: Inform users about safe enrollment, data usage policies, and fallback mechanisms.
Common Challenges & Solutions
- Spoofing & Presentation Attacks
• Solution: Implement advanced liveness detection and challenge-response protocols. - Privacy Concerns
• Solution: Use on-device template storage or decentralized identity frameworks (e.g., DID). - Algorithmic Bias
• Solution: Train models on diverse demographic datasets and conduct regular bias audits. - Interoperability
• Solution: Adopt industry standards (ISO/IEC 19794, FIDO2) to ensure cross-vendor compatibility. - Environmental Factors
• Solution: Use multimodal systems that compensate when one sensor underperforms (e.g., dusty fingerprints).
Future Trends in Biometric Authentication
- Behavioral Biometrics: Continuous authentication based on typing patterns, gait, and touchscreen gestures.
- Wearable Sensors: Smartwatches and earbuds capturing vein patterns, ECG, or perspiration signatures.
- Privacy-Preserving Biometrics: Homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation for matching without exposing raw data.
- AI-Enhanced Recognition: Deep-learning models that adapt to changing facial features, lighting conditions, and aging.
- Decentralized Identity & Blockchain: Self-sovereign identity wallets storing encrypted biometric proofs on a distributed ledger.
Conclusion
Biometric authentication is revolutionizing security by transforming unique biological traits into seamless, user-friendly credentials. By adhering to best practices, addressing privacy and bias concerns, and embracing emerging technologies, organizations and individuals can harness the full power of biometrics for real-world safety—every day, everywhere.
Elevate Your Competence: Uncover Our Insights on Techno
Read Our Most Recent Article About Digital Forensics: Uncovering Cyber Evidence and Investigating Digital Crimes!