JAKARTA, cssmayo.com – Data Lakes: Centralized Repositories for Raw and Processed Data ain’t just a hot topic—they totally changed the way I handle big messy datasets. Back in the day, I used to juggle spreadsheets, databases, and random folders. Let’s be real, it was a recipe for chaos (and a lot of lost sleep). Ever since I learned the ropes with data lakes, there’s no going back.
In the era of big data, the ability to store and process vast amounts of information has become a cornerstone for businesses and organizations. Data lakes have emerged as powerful solutions for managing both raw and processed data, providing a centralized repository that supports diverse analytical needs. My journey exploring data lakes has been insightful, revealing both their potential and the challenges they present.
What is a Data Lake?

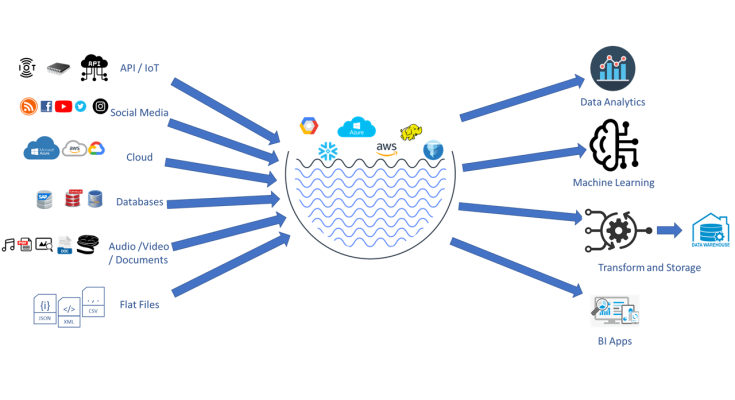
A data lake is a storage system that holds a vast amount of raw data in its native format until it is needed. Unlike traditional data warehouses, which store structured data in predefined schemas, data lakes can accommodate structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. This flexibility allows organizations to ingest data from a variety of sources, including databases, social media, IoT devices, and more.
Key Characteristics of Data Lakes
- Scalability: Data lakes are designed to scale horizontally, allowing organizations to store petabytes of data without significant performance degradation.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Utilizing commodity hardware and cloud storage solutions, data lakes can be more cost-effective than traditional data storage systems.
- Diverse Data Types: They can store various data formats, including text, images, video, and log files, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Schema-on-Read: Unlike traditional databases, where the schema is defined before data is stored, data lakes allow data to be stored first and analyzed later, enabling greater flexibility in data exploration.
My Experience with Data Lakes
My journey into the world of data lakes began when I was tasked with developing a data strategy for a mid-sized retail company. The organization was struggling with data silos, which hindered their ability to analyze customer behavior and sales trends effectively.
Initial Challenges
The first challenge was understanding how to integrate data from various sources, including point-of-sale systems, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and online platforms. The existing data architecture was rigid, making it difficult to adapt to new data sources. This experience highlighted the need for a more flexible solution, which led me to explore data lakes.
Implementation Journey
After thorough research, we decided to implement a data lake using a cloud-based solution. This decision was driven by the need for scalability and cost-effectiveness. We chose to use Amazon S3 as our storage solution, leveraging its durability and integration capabilities with other AWS services.
Data Ingestion
We implemented an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process to ingest data into the data lake. However, instead of transforming the data before loading it, we opted for a “raw data” approach, allowing us to store data as-is. This decision provided the flexibility to analyze the data later, depending on the specific use case.
Analyzing Data in the Lake
Once the data was ingested, we utilized tools like Amazon Athena and Apache Spark to perform analytics directly on the data lake. This approach allowed our team to run complex queries without the need for extensive data preparation. The ability to analyze both raw and processed data in one location proved invaluable for generating insights.
Real-World Tips for Implementing Data Lakes
Based on my experiences, here are some practical tips for successfully implementing and managing a data lake:
- Define Clear Objectives: Before implementing a data lake, define the specific business objectives you want to achieve. This clarity will guide your data ingestion and analysis strategies.
- Establish Data Governance: Implement robust data governance practices to ensure data quality and security. Define policies for data access, usage, and compliance to mitigate risks associated with data management.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select tools and technologies that align with your organization’s needs. Consider factors such as ease of use, integration capabilities, and support for various data formats.
- Plan for Data Lifecycle Management: Develop a strategy for managing data throughout its lifecycle, including data retention policies and archival processes. This planning will help optimize storage costs and maintain data relevance.
- Encourage a Data-Driven Culture: Foster a culture that encourages data exploration and analysis across the organization. Provide training and resources to empower employees to leverage the data lake effectively.
Conclusion
Data lakes represent a significant advancement in data management, offering organizations the flexibility to store and analyze diverse data types. My honest review of data lakes reflects both their potential and the challenges they present. By implementing best practices and focusing on clear objectives, organizations can harness the power of data lakes to drive insights and innovation. As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of big data, data lakes will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping their data strategies.
Explore our “Techno” category for more insightful content!
Don't forget to check out our previous article: Prosthetics Progress: Advanced Limbs and Organs Through Technology
For more information, visit our reference website: SITUSTOTO