JAKARTA, cssmayo.com – In the digital era, Cloud Resources have become the backbone of modern IT infrastructure, offering on-demand access to compute power, storage, networking, and specialized services. By leveraging cloud capabilities, organizations can innovate faster, scale seamlessly, and optimize costs. This article explores the types of cloud resources, strategies for effective utilization, best practices, and future trends to help you harness the full potential of the cloud.
1. Understanding Cloud Resources

1.1 What Are Cloud Resources?
Cloud resources refer to the virtualized components and services delivered over the internet by providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. They eliminate the need for upfront hardware investments and enable pay-as-you-go consumption.
1.2 Benefits of Leveraging Cloud Resources
- Scalability: Instantly adjust capacity based on demand.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for what you use; take advantage of spot instances and reserved capacity.
- Agility: Deploy new environments in minutes, accelerating development and testing.
- Global Reach: Provision resources in multiple regions for low-latency access and compliance.
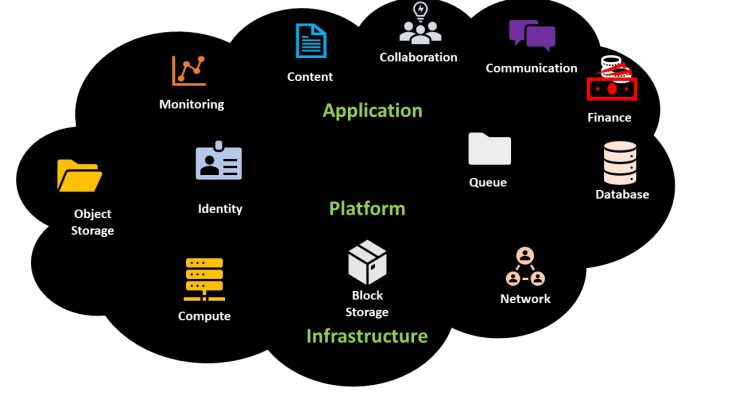
2. Core Types of Cloud Resources
2.1 Compute Services
- Virtual Machines (VMs) for full OS control
- Container orchestration (Kubernetes, ECS/EKS) for microservices
- Serverless functions (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions) for event-driven workloads
2.2 Storage and Database Services
- Object storage (S3, Azure Blob) for unstructured data
- Block storage (EBS, Azure Managed Disks) for high-performance volumes
- Managed databases (RDS, Cloud SQL) and NoSQL (DynamoDB, Cosmos DB)
2.3 Networking and Content Delivery
- Virtual private clouds (VPCs) for isolated networks
- Load balancers and API gateways for traffic management
- CDN services (CloudFront, Azure CDN) for global content distribution
2.4 Specialized and AI/ML Services
- AI/ML platforms (SageMaker, Vertex AI) for model training and deployment
- Big data analytics (EMR, Dataproc) and data warehousing (Redshift, BigQuery)
- IoT, blockchain, and other PaaS offerings
3. Strategies for Effective Cloud Resource Management
3.1 Right-Sizing and Autoscaling
Continuously monitor utilization metrics and adjust instance types or enable autoscaling groups to match workload patterns.
3.2 Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Use Terraform, CloudFormation, or ARM templates to define, version, and automate your Cloud Resources, ensuring consistency and repeatability.
3.3 Cost Optimization
- Leverage spot/preemptible instances for non-critical workloads
- Implement tagging policies to track spending by project or department
- Set budget alerts and use cost explorer tools for proactive management
3.4 Security and Compliance
- Enforce the principle of least privilege with IAM roles and policies
- Enable encryption at rest and in transit (TLS, KMS-managed keys)
- Regularly audit configurations using tools like AWS Config or Azure Policy
4. Best Practices
- Monitoring & Logging: Implement centralized logging (CloudWatch, Azure Monitor) and real-time alerts for anomalies.
- Backup & Disaster Recovery: Automate backups, define RTO/RPO objectives, and test recovery procedures.
- Governance & Policies: Establish organizational units, service control policies, and standardized naming conventions.
- DevOps Integration: Embed Cloud Resources provisioning into CI/CD pipelines to accelerate delivery and reduce human error.
5. Case Study: Scaling an E-Commerce Platform
A retail startup transitioned from on-premises servers to AWS to handle seasonal spikes:
- Migrated web servers to EC2 Auto Scaling groups behind an Application Load Balancer.
- Switched static assets to S3 with CloudFront for higher reliability and lower latency.
- Adopted RDS Aurora with Read Replicas to support intensive read-heavy workloads.
- Implemented Terraform for all infrastructure, reducing deployment time from days to hours.
Results:
- 4× improvement in page load times
- 30% reduction in operational costs
- Zero downtime during peak sale events
6. Future Trends in Cloud Resources
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Architectures: Seamlessly span workloads across public clouds and on-prem environments.
- Serverless & Edge Computing: Push compute closer to end users with Lambda@Edge and Azure Edge Zones.
- AI-Driven Resource Optimization: Autonomous scaling and cost management powered by machine learning.
- Green Cloud Initiatives: Sustainable data centers and carbon-aware compute scheduling.
Conclusion
By Thoughtfully leveraging Cloud Resources, organizations can achieve unprecedented agility, scalability, and cost savings. Adopting strategies like Right-sizing, Infrastructure as Code, and robust security practices will ensure you Maximize the value of your cloud investment. Stay informed about emerging trends to keep your architecture Future-proof and competitive.
Elevate Your Competence: Uncover Our Insights on Techno
Read Our Most Recent Article About Digital Communication: Enhancing Interaction in the Digital Age!