JAKARTA, cssmayo.com – Distributed Ledger Technology: The Foundation of Blockchain and Future Digital Systems is something I used to think sounded super intimidating—like, I’d hear “DLT” or “Techno blockchain” and my brain would just check out. But a couple of years back, I dove in, made a bunch of mistakes, and finally started to get it. If you’re curious or just tired of feeling lost when friends drop blockchain buzzwords, I hear you.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) underpins many of today’s hottest innovations—from cryptocurrencies to decentralized finance (DeFi) and beyond. In this deep dive, I’ll walk you through:
- A clear definition of DLT
- Why it’s transforming industries
- My personal “aha” moments exploring ledgers
- Core principles and real-world applications
- A practical how-to guide and best practices
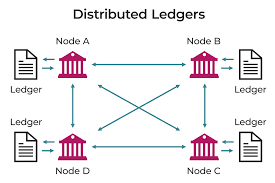
What Is Distributed Ledger Technology?

Distributed Ledger Technology is a decentralized database spread across multiple nodes (computers or servers), where:
- Each node holds an identical, append-only copy of the ledger
- Consensus mechanisms ensure agreement on the ledger’s state
- Cryptographic techniques guarantee data integrity and immutability
Unlike traditional centralized databases, DLT removes single points of failure and opens up new possibilities for trustless transactions.
Why DLT Matters
- Enhanced Security
• Tamper-resistance via cryptographic hashing and consensus. - Transparency & Auditability
• Every transaction is time-stamped and visible to permitted participants. - Decentralization
• No single authority controls the network—resilience against outages and censorship. - Efficiency & Cost Savings
• Streamlined settlement processes, reduced intermediaries, and lower reconciliation costs. - Programmability
• Smart contracts automate business logic without manual intervention.
My Surprising Discoveries
- Discovery 1: Consensus Isn’t One-Size-Fits-All
I assumed proof-of-work (PoW) was the de facto standard—then I explored proof-of-stake (PoS), delegated PoS, and Byzantine Fault Tolerance variants. Each has unique trade-offs between speed, security, and energy usage. - Discovery 2: Private vs. Public Ledgers
Private (permissioned) ledgers excel in enterprise settings, while public chains spur open innovation. I built a small Hyperledger Fabric network to see first-hand how access controls shape performance. - Discovery 3: Cross-Chain Interoperability Is the Next Frontier
Bridging assets and data across ledgers is more complex than I imagined. Projects like Polkadot, Cosmos, and IBC protocols are solving this puzzle—but interoperability standards are still evolving.
Core Principles of DLT
- Decentralization: Distribution of data and control
- Consensus Mechanisms: Algorithms like PoW, PoS, PBFT, etc.
- Immutability: Once recorded, transactions cannot be altered
- Cryptography: Digital signatures and hashing for security
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing code governing transactions
Real-World Use Cases
- Finance & Payments
• Cross-border remittances, tokenized assets, and decentralized exchanges - Supply Chain Management
• Provenance tracking from raw materials to finished goods - Identity & Credentialing
• Self-sovereign identity platforms that put individuals in control - Healthcare Records
• Secure, interoperable patient data with audit trails - Voting & Governance
• Transparent, tamper-proof election systems and DAO frameworks
Step-by-Step Guide to Exploring DLT
- Choose Your Network
- Public (Ethereum, Solana) vs. Private (Hyperledger Fabric, Corda)
- Set Up a Node
- Follow official docs to install client software and sync the ledger.
- Learn Smart Contract Development
- Solidity for Ethereum, Chaincode for Fabric, Rust for Solana.
- Experiment with Testnets
- Use free tokens to deploy contracts and interact with DApps.
- Explore SDKs & APIs
- Web3.js, ethers.js, Hyperledger SDKs to build front-end interfaces.
- Join Community Channels
- Discord, Telegram, Stack Exchange to ask questions and share insights.
- Deploy a Simple DApp
- Create a token, build a wallet interface, or a supply chain tracker.
Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
- Pitfall: Ignoring Network Fees
Fix: Monitor gas prices and optimize contract code to reduce costs. - Pitfall: Weak Key Management
Fix: Use hardware wallets, secure key vaults, and multi-signature schemes. - Pitfall: Overcomplicating Smart Contracts
Fix: Keep logic lean; audit code and leverage battle-tested libraries. - Pitfall: Assuming Immutability Solves All Trust Issues
Fix: Combine on-chain proofs with off-chain audits and governance processes.
Tools & Resources
- Blockchain Explorers (Etherscan, Solscan)
- Development Frameworks (Truffle, Hardhat, Brownie)
- Wallets & Key Management (MetaMask, Ledger, Trezor)
- Interoperability Protocols (Polkadot, Cosmos SDK, Wormhole)
- Learning Platforms (CryptoZombies, ConsenSys Academy, Coursera)
Future Outlook
- Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
• Rollups, sidechains, and state channels to boost throughput. - Decentralized Identity & Web3
• Universal DID standards for seamless authentication. - Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
• Governments exploring DLT for programmable, sovereign digital money. - Tokenized Real-World Assets
• Fractional ownership of real estate, art, and commodities on-chain.
Conclusion
Distributed Ledger Technology is more than a buzzword—it’s a paradigm shift in how we store, verify, and exchange value. Whether you’re a developer, entrepreneur, or curious learner, diving into DLT will equip you with the tools to shape tomorrow’s digital systems. Embrace the principles of decentralization, experiment responsibly, and stay engaged with the vibrant global community. Your journey into the ledger-powered future starts now!
Elevate Your Competence: Uncover Our Insights on Techno
Read Our Most Recent Article About Weaponized AI Ethics: Addressing the Moral and Societal Implications of Autonomous Weapons!