JAKARTA, cssmayo.com – In the fast-paced world of IT, the ability to adapt to change is crucial for project success. Agile methodology has developed into a robust framework that enables teams to swiftly adapt to changing requirements and produce high-quality software. This article delves into the principles of Agile methodology, its benefits, and practical strategies for implementing it effectively in IT projects.
What is Agile Methodology?

Understanding Agile Methodology
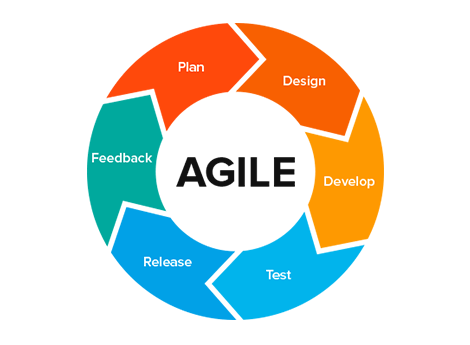
Agile methodology is an iterative approach to software development that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer-centricity. Unlike traditional waterfall models, which follow a linear sequence of phases, Agile promotes continuous improvement and adaptive planning throughout the project lifecycle.
The Agile Manifesto
The foundation of Agile methodology is the Agile Manifesto, which outlines four key values:
- Individuals and Interactions over processes and tools.
- Working Software over comprehensive documentation.
- Customer Collaboration over contract negotiation.
- Responding to Change over following a plan.
These values highlight the importance of people, collaboration, and adaptability in successful project delivery.
Agile Methodology Priciple Key
1. Iterative Development
Agile promotes iterative development, where projects are divided into small, manageable increments known as iterations or sprints. Each iteration typically lasts from one to four weeks and involves:
- Planning: Defining goals and deliverables for the iteration.
- Execution: Developing and testing features within the iteration.
- Review: Demonstrating completed work to stakeholders for feedback.
2. Continuous Feedback
Regular feedback is a cornerstone of Agile methodology. Teams engage with stakeholders throughout the project to ensure that the product aligns with customer needs. This involves:
- Sprint Reviews: At the end of each iteration, teams present their work to stakeholders for evaluation.
- Retrospectives: Teams reflect on their processes and outcomes to identify areas for improvement.
3. Cross-Functional Teams
Agile encourages the formation of cross-functional teams that include members with diverse skills. This collaboration enhances problem-solving and innovation, as team members can contribute their expertise across various domains, including development, testing, and design.
4. Embracing Change
One of the core tenets of Agile methodology is the acceptance of change, even late in the development process. Agile teams prioritize flexibility, allowing them to adjust their plans based on new information, customer feedback, or shifting market conditions.
Benefits of Agile Methodology
1. Increased Flexibility
Agile methodology enables teams to adapt quickly to changing requirements, ensuring that the final product meets customer expectations. This flexibility reduces the risk of delivering a product that does not align with market needs.
2. Enhanced Collaboration
By fostering open communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders, Agile creates a shared understanding of project goals. This collaborative environment leads to better decision-making and more effective problem-solving.
3. Improved Quality
Continuous testing and feedback throughout the development process help identify and address issues early. This proactive approach results in higher-quality software that meets user needs and reduces the likelihood of costly post-release fixes.
4. Faster Time to Market
Agile teams deliver working software incrementally, allowing organizations to release features and updates more frequently. This rapid delivery enhances customer satisfaction and provides a competitive advantage.
Implementing Agile Methodology in IT Projects
1. Choose an Agile Framework
There are several Agile frameworks to choose from, including:
- Scrum: A popular framework that organizes work into time-boxed sprints and emphasizes roles such as Scrum Master and Product Owner.
- Kanban: A visual approach that focuses on managing work in progress and optimizing flow.
- Extreme Programming (XP): A framework that emphasizes technical excellence and frequent releases.
Selecting the right framework depends on the specific needs and context of your project.
2. Establish a Collaborative Culture
Creating a culture that supports collaboration and open communication is essential for Agile success. Strategies include:
- Daily Stand-Ups: Short meetings where team members share progress, challenges, and plans for the day.
- Open Feedback Channels: Encouraging team members to provide and receive feedback regularly.
3. Prioritize User Stories
User stories are short, simple descriptions of features from the end-user perspective. Prioritizing user stories helps teams focus on delivering the most valuable features first. Techniques for prioritization include:
- MoSCoW Method: Categorizing features as Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, or Won’t-have.
- Value vs. Effort Matrix: Evaluating features based on their value to users versus the effort required to implement them.
4. Use Agile Tools
Leveraging Agile project management tools can enhance visibility and collaboration. Popular tools include:
- Jira: A widely used tool for tracking issues and managing Agile projects.
- Trello: A visual tool that utilizes boards and cards to arrange tasks and manage workflows.
- Asana: A task management tool that helps teams track progress and collaborate effectively.
Real-World Examples of Agile Methodology
1. Case Study: Spotify
Spotify employs Agile practices to support its rapid growth and dynamic environment. By organizing teams into autonomous squads, Spotify fosters innovation and collaboration. Key outcomes include:
- Faster feature development and deployment.
- High levels of employee engagement and ownership.
2. Case Study: ING Bank
ING Bank adopted Agile methodology to enhance its digital banking services. By restructuring teams and implementing Agile practices, ING achieved:
- Improved customer satisfaction through faster delivery of new features.
- Enhanced collaboration across departments, leading to more effective problem-solving.
Conclusion
Agile methodology offers a powerful framework for adapting to change in IT projects. By embracing iterative development, continuous feedback, and cross-functional collaboration, organizations can enhance their ability to deliver high-quality software that meets customer needs.
As the technology landscape continues to evolve, adopting Agile methodology will be essential for organizations looking to stay competitive and responsive to market demands. By fostering a culture of adaptability and collaboration, teams can navigate the complexities of software development like a pro.
Elevate Your Competence: Uncover Our Insights on Techno
Read Our Most Recent Article About IT Risk!